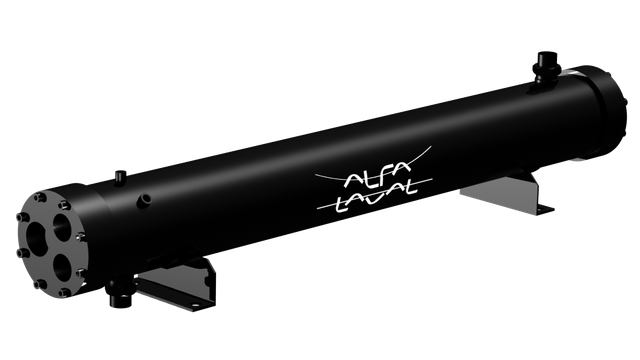
CXP
The Alfa Laval CXP is a compact condenser for fresh water applications that use HCFC or HFC refrigerants at medium and high pressures (30 - 45 barg). Capacity range 5 - 150 kW. PED/CE, EAC, SELO, DNV and other major marine approvals are available.
Alfa Laval CXP series – for applications using R404 refrigerants
For lower capacity requirements, the Alfa Laval CXP series is ideal as it is specially designed to use smaller tubing for up to 150 kW. This series is suitable for (among others) R404 refrigerants.
Options
- ASME, EAC, SELO, DNV and other major marine approvals available upon request
- Mounting feet
- Sight glass
- Desuperheater version
Benefits
- Compact design vs equivalent products in the market
- Flexibility: modular header for 2 and 4 passes
- Performance guarantee by Alfa Laval lab test
- Configurable online: contact Alfa Laval local sales organization to get the login
Fonctionnement
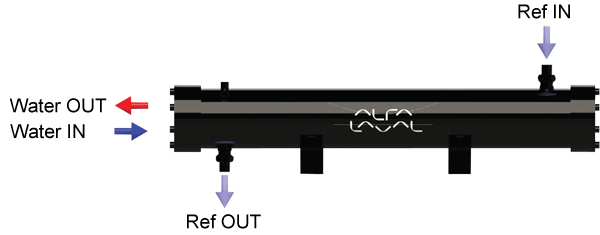
All fresh-water condensers are shell-and-tube heat exchangers with a primary fluid - normally a two-phase HFC refrigerant - flowing in the shell side and a secondary - pure water or water with some antifreeze brine added - running in the tube side.
Fresh-water condensers are designed for use as one component in cooling systems which consists of compressor, condenser, evaporator and expansion valve. The two-phase refrigerant arrives at the condenser in vapour from the compressor at high temperature and pressure.
The refrigerant enters in the condenser from the connection placed in the upper side of the shell and it is distributed all over the shell thanks to an impingement plate. The contact of the high-pressure hot-vapour refrigerant with the enhanced surface of the tubes - which are carrying the cooling water - causes the condensation.
When the condensation process is complete, the refrigerant is slightly subcooled in order to avoid vapour bubbles reaching the expansion valve. Thanks to the high performance tubes, this free condensation process ensures a lower condensing temperature which results in high efficiency of the cooling system.
The cooling water source can be a cooling tower, a drycooler, a well, a river, a lake or an industrial process. On the water side, two couples of headers and gaskets are designed with single, two or four passes configuration in order to ensure the right water velocity and pressure drop values for each application.